· アーキテクチャ設計 · 3 min read
Google Cloud でのマイクロサービスアーキテクチャの実装
実際のユースケースに基づいた、Google Cloud でのマイクロサービス実装の具体的な手順とベストプラクティス
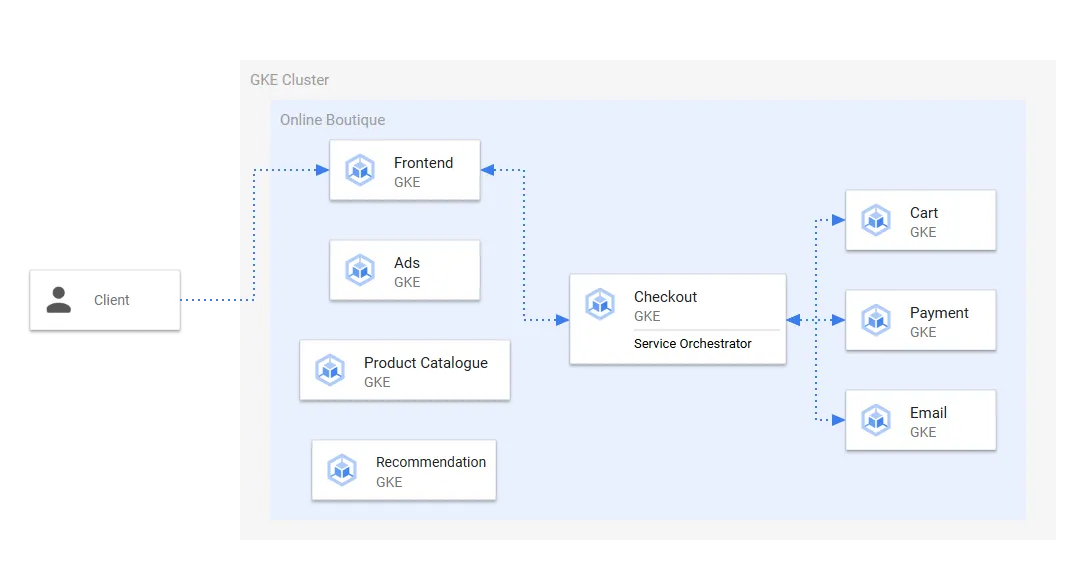
ECサイトをマイクロサービス化する
一般的なECサイトを例に、モノリシックなアプリケーションをマイクロサービスに分割する実践的な手順を説明します。
分割するサービスと使用するGoogle Cloudサービス
認証サービス
- Cloud Run + Cloud SQL
- Firebase Authentication
商品カタログサービス
- Cloud Run + Firestore
- Cloud Storage(画像保存用)
注文サービス
- Cloud Run + Cloud Spanner
- Cloud Pub/Sub(在庫更新通知)
決済サービス
- Cloud Functions
- Secret Manager(API キー管理)
認証サービスの実装
Firebase Authentication との統合
from firebase_admin import auth, initialize_app
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
initialize_app()
@app.route('/verify-token', methods=['POST'])
def verify_token():
token = request.headers.get('Authorization', '').split('Bearer ')[1]
try:
decoded_token = auth.verify_id_token(token)
return {'user_id': decoded_token['uid']}, 200
except Exception as e:
return {'error': str(e)}, 401
Cloud Run へのデプロイ
# コンテナのビルドとデプロイ
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/auth-service
gcloud run deploy auth-service \
--image gcr.io/${PROJECT_ID}/auth-service \
--platform managed \
--region asia-northeast1 \
--allow-unauthenticated
商品カタログサービスの実装
Firestore データモデル
from google.cloud import firestore
db = firestore.Client()
class Product:
def __init__(self, id, name, price, stock):
self.id = id
self.name = name
self.price = price
self.stock = stock
@staticmethod
def from_dict(source):
return Product(
id=source['id'],
name=source['name'],
price=source['price'],
stock=source['stock']
)
def to_dict(self):
return {
'id': self.id,
'name': self.name,
'price': self.price,
'stock': self.stock
}
def save(self):
db.collection('products').document(self.id).set(self.to_dict())
商品画像の処理
from google.cloud import storage
def upload_product_image(product_id, image_file):
client = storage.Client()
bucket = client.bucket('your-product-images-bucket')
blob = bucket.blob(f'products/{product_id}.jpg')
blob.upload_from_file(image_file)
return blob.public_url
サービス間通信の実装
Pub/Sub を使用した在庫更新
from google.cloud import pubsub_v1
publisher = pubsub_v1.PublisherClient()
topic_path = publisher.topic_path('your-project', 'inventory-updates')
def notify_stock_update(product_id, new_stock):
data = {
'product_id': product_id,
'new_stock': new_stock,
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
future = publisher.publish(
topic_path,
data=json.dumps(data).encode('utf-8')
)
return future.result()
本番環境での運用
監視とアラートの設定
- Cloud Run サービスの可用性監視
# uptime-check.yaml
checkConfig:
httpCheck:
path: "/health"
port: 443
period: "300s"
timeout: "10s"
threshold:
failure: 3
success: 1
- エラーレートアラート
from google.cloud import monitoring_v3
def create_error_alert(project_id):
client = monitoring_v3.AlertPolicyServiceClient()
alert_policy = {
"display_name": "High Error Rate Alert",
"conditions": [{
"display_name": "error_rate_condition",
"condition_threshold": {
"filter": 'metric.type="run.googleapis.com/request_count" '
'resource.type="cloud_run_revision" '
'metric.labels.response_code_class="5xx"',
"duration": {"seconds": 300},
"comparison": "COMPARISON_GT",
"threshold_value": 5.0,
}
}],
"notification_channels": [
f"projects/{project_id}/notificationChannels/{channel_id}"
],
}
policy = client.create_alert_policy(
request={"name": f"projects/{project_id}",
"alert_policy": alert_policy}
)
return policy
📚 より詳しく学びたい方へ
「Google Cloud でのマイクロサービス実践ガイド」 https://amzn.to/4eA8iIJ
コストの最適化とスケーリング
Cloud Run の最適な設定
# メモリと CPU の最適化
gcloud run services update product-service \
--memory 512Mi \
--cpu 1 \
--min-instances 1 \
--max-instances 10 \
--concurrency 80



